walnuts
High Heat, Low Demand Hurt Walnut Crop
By Christine Souza, California Farm Bureau
California farmers are tearing out walnut orchards, such as at this farm near Winters, in response to quality concerns due to a September heat wave, lower demand and prices, and other market issues. The California Walnut Commission estimates $1 billion in damages to the 2022 crop.
Walnut farmers are tearing out older trees and less desirable varieties as the price for the nut has plummeted well below the cost of production, causing some growers to rethink walnuts and look for alternative crops.
“I’ve seen several younger orchards that have come out already in Fresno, Merced and Madera counties,” said Kings County farmer Brian Medeiros of Hanford, who farms walnuts, almonds and row crops. “My neighbor had a walnut orchard that was about six years old, and he tore the whole thing out. He just said, ‘I’m losing money hand over fist. I’m not going to keep doing it.’”
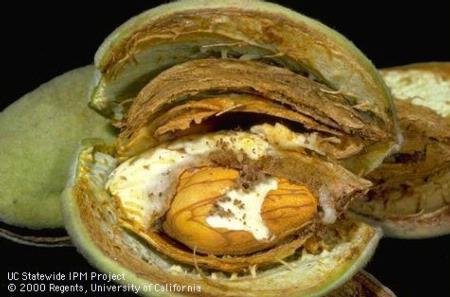
A heat wave last September cooked the walnuts on the trees during a critical time of the growing cycle. High temperatures were followed by rain that led to mold problems.
“We had extremely high temperatures—up to 117 degrees for three to four days in some areas—and this occurred when walnuts were at their most sensitive stage in growth,” said Robert Verloop, president and chief executive officer of the California Walnut Board and California Walnut Commission. “We conducted our own informal survey of about 75% of the industry and documented pretty clearly that the range is anywhere from 30% to 40% of the (walnut) volume that was impacted. That means if the handler opens up 100 pounds of walnuts, 30 to 40 pounds is absolutely not usable.”
Walnut growers in Stanislaus County demonstrated to the county agricultural commissioner that there was 36% loss in crop volume, Verloop said. The growers provided damage information within the required 60 days, which led to a federal disaster declaration.
On Jan. 13, U.S. Agriculture Secretary Tom Vilsack designated a disaster declaration for Stanislaus County and contiguous counties of Alameda, Calaveras, Mariposa, Merced, San Joaquin, Santa Clara and Tuolumne for walnut losses due to the heat wave last September.
Farmers in qualifying counties have eight months from the date of the declaration to apply for emergency loans through the U.S. Department of Agriculture Farm Service Agency. The California Walnut Commission is working with federal lawmakers on additional aid, including walnut purchases by USDA for food banks and tree-pull programs.
With the price to growers for the 2022 walnut crop at about 40 cents per pound or less—and well below last year’s break-even price of between 70 and 90 cents per pound—walnuts were the obvious choice for removal for Medeiros, he said. He pulled out 16 acres of walnut trees to scale down his water use to comply with groundwater regulations and manage his allotment.
“Our orchard is only 15 years old, so when I was pulling out those 16 acres, it literally broke my heart because I’m pulling out beautiful trees that look gorgeous, and I’m bulldozing them over,” Medeiros said. “The (walnut) price is making it much easier, much quicker for us to move ahead because—unless this price changes dramatically in the coming year or we have some outstanding support from USDA—we’re probably pulling the rest of them out next year.”
Stanislaus County farmer Gordon Heinrich of Modesto, who farms walnuts and operates a huller and dehydrator, said the price of walnuts is at a 30-year low, and input costs have gone up substantially.
“We’re actually operating below the cost of production right now, and everybody’s scratching their heads trying to figure out where you can cut back on your inputs to survive this market situation,” Heinrich said.
“There’s not a lot of places you can cut,” he added.
Handlers are advising walnut growers to remove older, darker-kernel varieties such as Vina, Serr and Hartley, to maintain the supply of light walnuts, Chandler, Tulare and Howard, that global buyers demand.
“Growers are starting to realize that all those older varieties need to be taken out and replanted with a more modern variety, such as a Chandler,” Heinrich said. “The quicker that we can change our market strategy as far as being able to put a better product on the market, the longer this is going to last. It is going to right itself in time, but there’s a lot of farmers out there who are going to have a real tough time.”
Verloop said handlers reported 20% to 50% of the 2022 walnut crop was substandard in quality and is better suited for cattle feed. He said the commission estimates the farm-gate loss to growers is $1 billion.
Aside from quality problems, Verloop said many different factors affect the market for California walnuts, much of which are exported to Europe, Turkey, India, Spain, Japan, Korea and the Middle East.
“The problem is the pipeline to the consumer has a lot of walnuts in it already,” Verloop said. The carryover from the 2021 crop of about 135,000 tons, he said, and the 2022 crop is expected to be between 750,000 tons to 780,000 tons and much larger than the 720,000-ton crop forecast last September.
Retaliatory trade tariffs and the COVID-19 pandemic added to the walnut supply-demand imbalance and led to trucking and transportation challenges, congestion at the ports and a slowing of consumer demand. Inflation, the higher value of the dollar and the war in the Ukraine also are affecting customer confidence and buying power, Verloop said.
“We’re in the middle of that perfect storm,” Heinrich said of the global and economic stressors impacting the walnut market. “We’re hoping that we can just hang on. We’re lucky with our operation that we’re somewhat diversified, but even almonds are struggling with some of the same problems.”
Bill Carriere, president of Carriere Family Farms—a grower, processor and marketer of walnuts in Glenn County—said it is a very nervous time for growers and handlers.
“Sales were slow in general, and you had quality concerns that doubled the problem. That really hurt storage, so our storage is full. There are walnuts in warehouses that are not normally in warehouses,” said Carriere, who added that 20% of the 2022 walnut crop he received is not salable. “In our operation, we’re losing much more money as a grower than we are as a handler, but we’re losing in both.”
To recover from this year’s challenges, Verloop said, “the goal right now is to remove all of the substandard quality product off the market and let the good quality product price start to come up a little bit.”
For the next year or two, Verloop said he expects a downsizing of the walnut sector as growers remove less productive acres and less desirable heritage walnut varieties.
“We’re working with all of our trade agencies around the world to take a look at what can we do to recover from this year,” Verloop said. “We think there’s a lot of trust and confidence long term in our product from California because it’s been the gold standard. We’re working hard on several different fronts to make sure that we’re better positioned in the future.”
Growers seeking more information about disaster assistance and other program relief are encouraged to contact their local Farm Service Agency.