New Dietary Guidelines for Healthy Eating
HHS and USDA Release New Dietary Guidelines to Encourage Healthy Eating Patterns to Prevent Chronic Diseases
Secretary of Health and Human Services Sylvia M. Burwell and Secretary of Agriculture Tom Vilsack TODAY released updated nutritional guidelines that encourage Americans to adopt a series of science-based recommendations to improve how they eat to reduce obesity and prevent chronic diseases like Type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease. The 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans is the nation’s trusted resource for evidence-based nutrition recommendations and serves to provide the general public, as well as policy makers and health professionals with the information they need to help the public make informed choices about their diets at home, school, work and in their communities.
The newly released 8th edition of the Dietary Guidelines reflects advancements in scientific understanding about healthy eating choices and health outcomes over a lifetime. This edition recognizes the importance of focusing not on individual nutrients or foods in isolation, but on the variety of what people eat and drink—healthy eating patterns as a whole—to bring about lasting improvements in individual and population health.
“The Dietary Guidelines for Americans is one of many important tools that help to support a healthier next generation of Americans,” said Secretary Vilsack. “The latest edition of the Dietary Guidelines provides individuals with the flexibility to make healthy food choices that are right for them and their families and take advantage of the diversity of products available, thanks to America’s farmers and ranchers.”
The specific recommendations fit into five overarching guidelines in the new edition:
1. Follow a healthy eating pattern across the lifespan. Eating patterns are the combination of foods and drinks that a person eats over time.
2. Focus on variety, nutrient-dense foods, and amount
3. Limit calories from added sugars and saturated fats, and reduce sodium intake
4. Shift to healthier food and beverage choices
5. Support healthy eating patterns for all
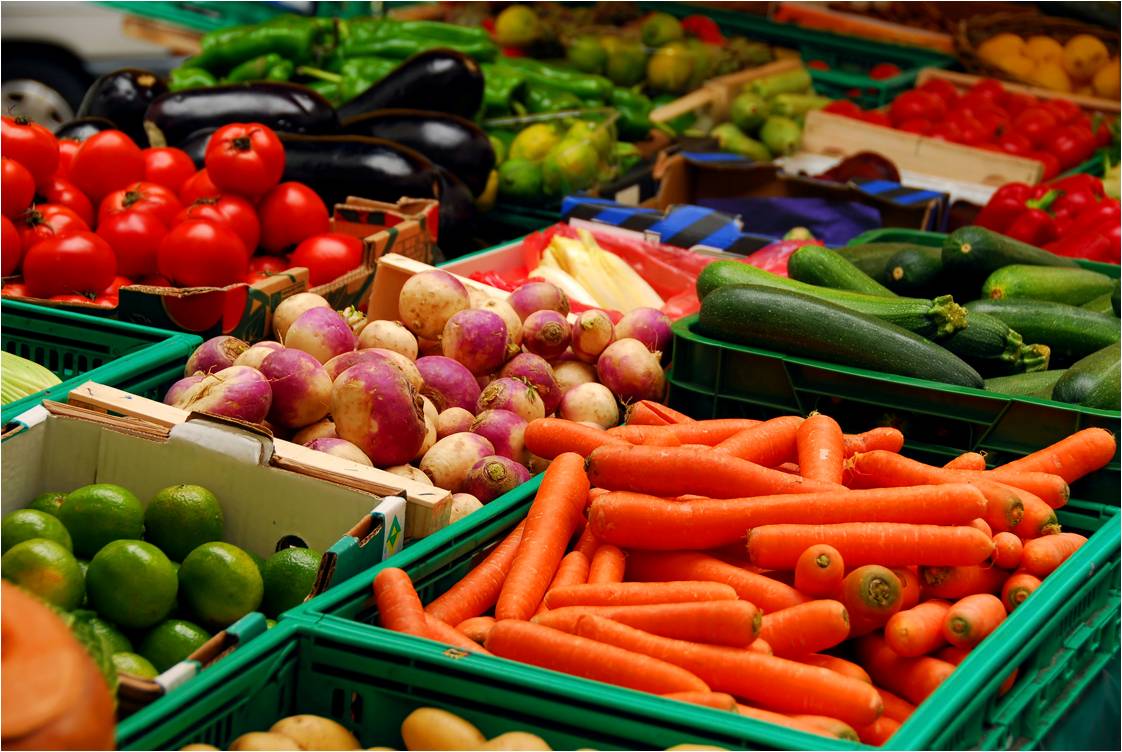
Healthy eating patterns include a variety of nutritious foods like vegetables, fruits, grains, low-fat and fat-free dairy, lean meats and other protein foods and oils, while limiting saturated fats, trans fats, added sugars and sodium. A healthy eating pattern is adaptable to a person’s taste preferences, traditions, culture and budget.
Importantly, the guidelines suggest Americans should consume:
1. A variety of vegetables, including dark green, red and orange, legumes (beans and peas), starchy and other vegetables
2. Fruits, especially whole fruits
3. Grains, at least half of which are whole grains
4. Fat-free or low-fat dairy, including milk, yogurt, cheese, and/or fortified soy beverages
5. A variety of protein foods, including seafood, lean meats and poultry, eggs, legumes (beans and peas), soy products, and nuts and seeds
6. Oils, including those from plants: canola, corn, olive, peanut, safflower, soybean, and sunflower. Oils also are naturally present in nuts, seeds, seafood, olives, and avocados.
Further, Americans should be encouraged to consume:
1. Less than 10 percent of calories per day from added sugars. ChooseMyPlate.gov provides more information about added sugars, which are sugars and syrups that are added to foods or beverages when they are processed or prepared. This does not include naturally occurring sugars such as those consumed as part of milk and fruits.
2. Less than 10 percent of calories per day from saturated fats. The Nutrition Facts label can be used to check for saturated fats. Foods that are high in saturated fat include butter, whole milk, meats that are not labeled as lean, and tropical oils such as coconut and palm oil.
3. Less than 2,300 milligrams (mg) per day of sodium for people over the age of 14 years and less for those younger. The Nutrition Facts label is a helpful tool to check for sodium, especially in processed foods like pizza, pasta dishes, sauces, and soups.
Based on a review of current scientific evidence on nutrition, the 2015 edition includes updated guidance on topics such as added sugars, sodium, and cholesterol and new information on caffeine. For example, the 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines is the first edition to:
1. Recommend a quantitative limit to consume less than 10 percent of calories from added sugars.
2. Reaffirm guidance about the core building blocks of a healthy lifestyle that have remained consistent over the past several editions
3. Suggest there is still work to be done to encourage more Americans to follow the recommendations outlined in the Dietary Guidelines.
The 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines continues the nation’s dependence on California agriculture, which includes more than 400 commodities. According to the California Department of Food and Agriculture (CDFA) in 2014, the state produced nearly half of US-grown fruits, nuts and vegetables. Across the nation, US consumers regularly purchase several crops produced solely in California.
California’s top-ten valued commodities (USDA/NASS Crop Year Report 2014):
* Milk — $9.4 billion
* Almonds — $5.9 billion
* Grapes — $5.2 billion
* Cattle, Calves — $3.7 billion
* Strawberries — $2.5 billion
* Lettuce — $2 billion
* Walnuts — $1.8 billion
* Tomatoes — $1.6 billion
* Pistachios — $1.6 billion
* Hay — $1.3 billion
The 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans is available at dietaryguidelines.gov.USDA has also released updates for consumers on ChooseMyPlate.gov, and new resources will soon be available on Health.gov from HHS that will help health professionals support their clients and patients in making healthy choices.
The Dietary Guidelines is required under the 1990 National Nutrition Monitoring and Related Research Act, which states that every 5 years, the U.S. Departments of Health and Human Services (HHS) and of Agriculture (USDA) must jointly publish a report containing nutritional and dietary information and guidelines for the general public. The statute requires that the Dietary Guidelines be based on the preponderance of current scientific and medical knowledge.