Fighting to Protect Family Farms from Water Diversion
In Face of Water Diversion Threat, Ag Industry Experts are Speaking Out
By Laurie Greene, Editor
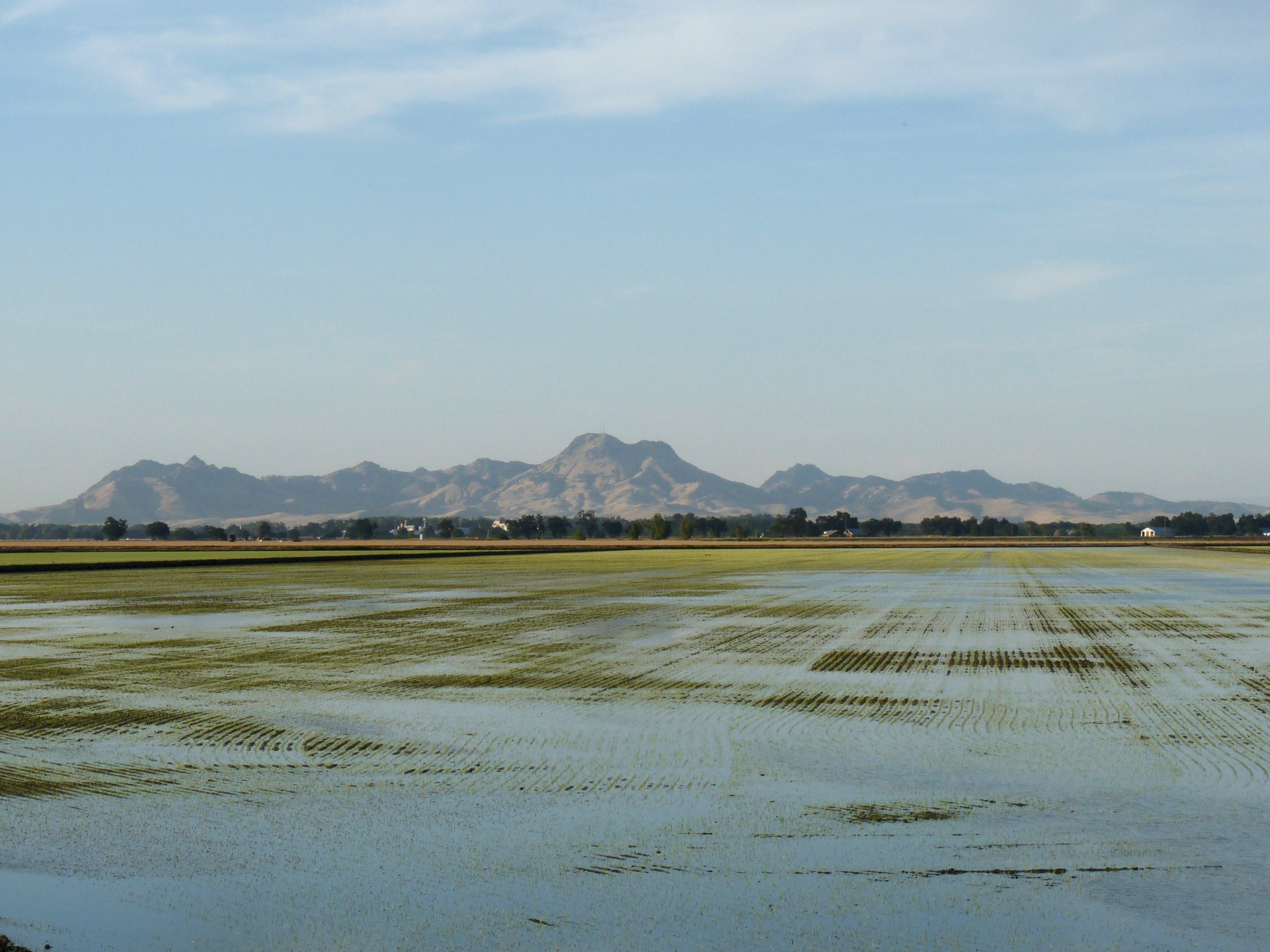
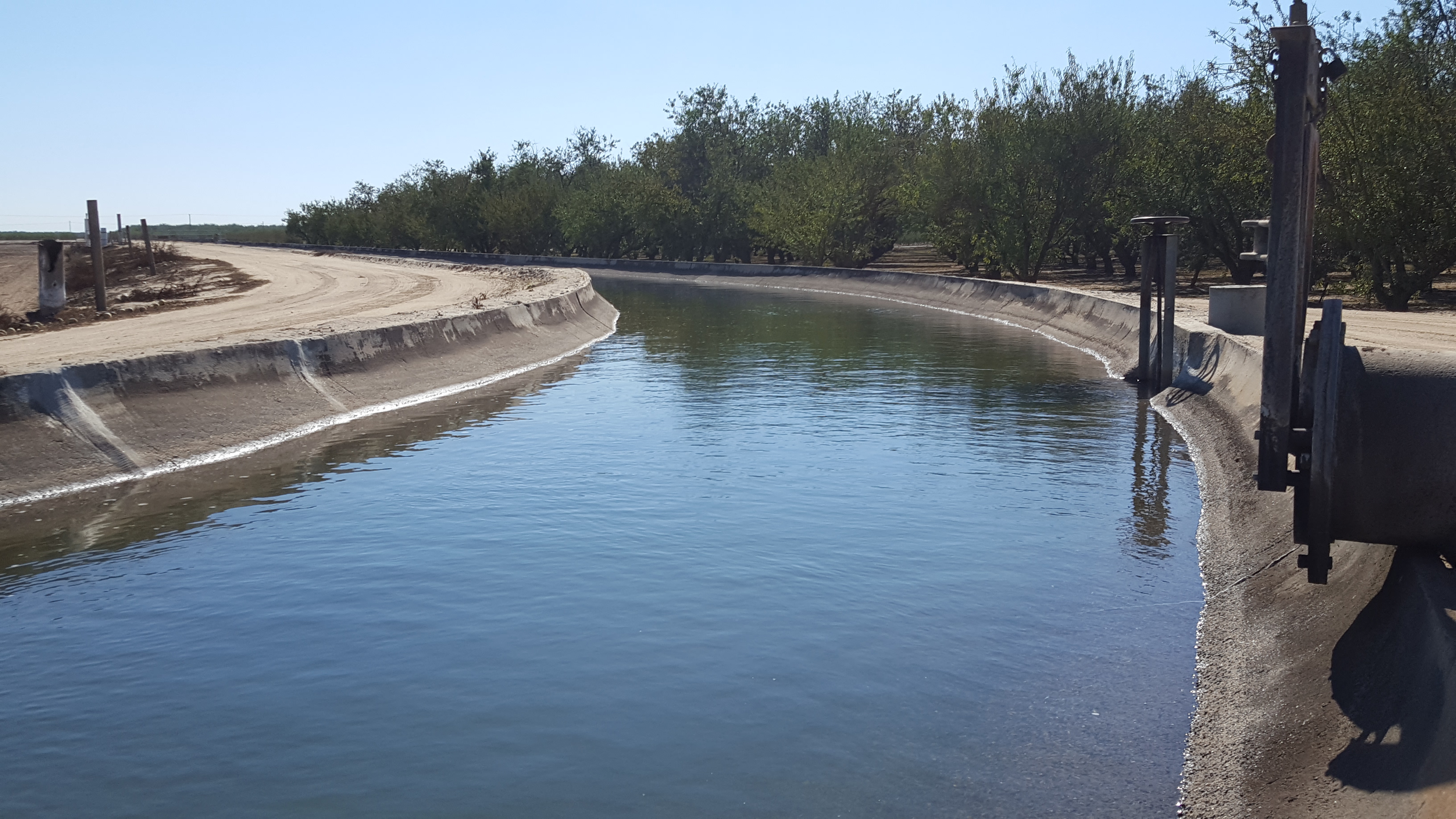
California Ag Today has been reporting on the California State Water Resources Control Board’s (SWRCB) proposed plan to divert 40 percent of the surface water from the Tuolumne River and two additional tributaries of the San Joaquin River between February 1st and June 30th every year. The SWRCB plan is designed to increase flows in the Delta in an effort to help the declining smelt and salmon populations. Yet, these water diversions would severely impact not only the farm industry, but communities in the Modesto and Turlock Irrigation Districts as well.
Ag officials say this is yet another threat to family farms in an attempt to protect the smelt and salmon. Farmers would lose a major portion of their surface water and be forced to pump more groundwater.
“Farming is not just a job; it’s a way of life for many of these families. And that livelihood, that way of life, is being threatened,” said Michael Boccadoro, president of West Coast Advisors, an independent, nonpartisan public affairs and advocacy firm that specializes in complex and often controversial public issues in Sacramento.
Boccadoro said the farm industry in the region is not sitting still while all of this is happening. There is a website, worthyourfight.org, that addresses this new assault on agriculture.
“It is worth fighting for,”said Boccadoro. “I was born and raised in agriculture, and I still think it’s a wonderful lifestyle. We need to protect it at all costs. This is starting to border on the ridiculous in terms of just one issue after another. . . This is not a “Mother Nature” issue; this is government putting these obstacles and these problems in front of agriculture, and that’s troubling.”
“We produce much of the fruits and vegetables and nearly all the nut crops for the entire nation. So, of course, we would expect to see significant amounts of water being used by farming in California,” Boccadoro said.
“It’s just reality, and for whatever reason, I think people have been misled and don’t understand this is just part of growing food. Like I have said, if you are concerned about it, all you’ve got to do is quit eating. It’s that simple.”
Links: