Pests and Diseases
Push Back NOW with Orchard Sanitation
Part One of a Series
Orchard Sanitation Critical This Season
By Patrick Cavanaugh, Farm News Director
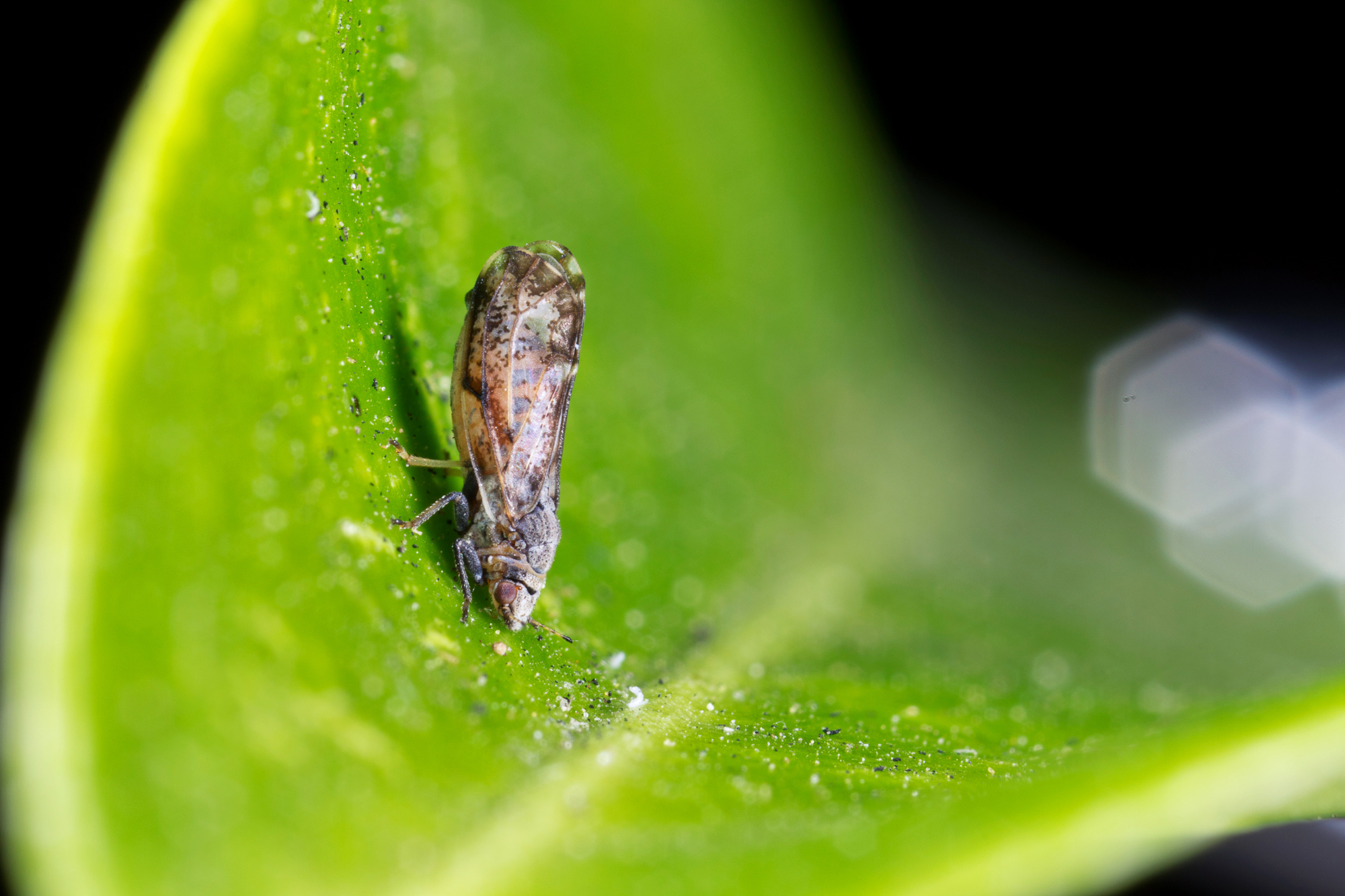
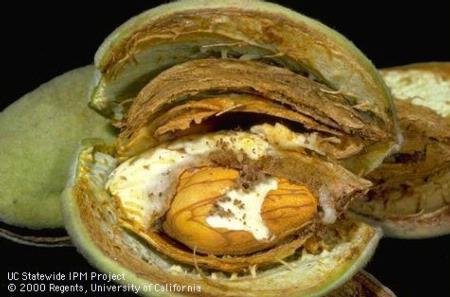
We recently spoke with Emily Symmes, the UC Area Integrated Pest Management farm advisor for the Sacramento Valley in statewide IPM program. She told California Ag Today about few reasons as to why Navel Orangeworm damage was so devastating this year, costing tree nut growers at least $137 million.
NOW is ubiquitous. And the nut crop footprint in California is larger, with one million acres of almonds, along with pistachios and walnuts up and down the San Joaquin valley.
“The pest is not going anywhere,” Symmes said.
“We had a lot of unique circumstances. The amount of rainfall we got in late 2016 into 2017 was unprecedented and led us into a bad navel orange worm year because growers couldn’t get out and sanitize their orchards”
“Growers were not able to get into their orchards because of standing water,” Symmes explained.
Also, rainfall and moist conditions can help NOW mortality in the winter. “
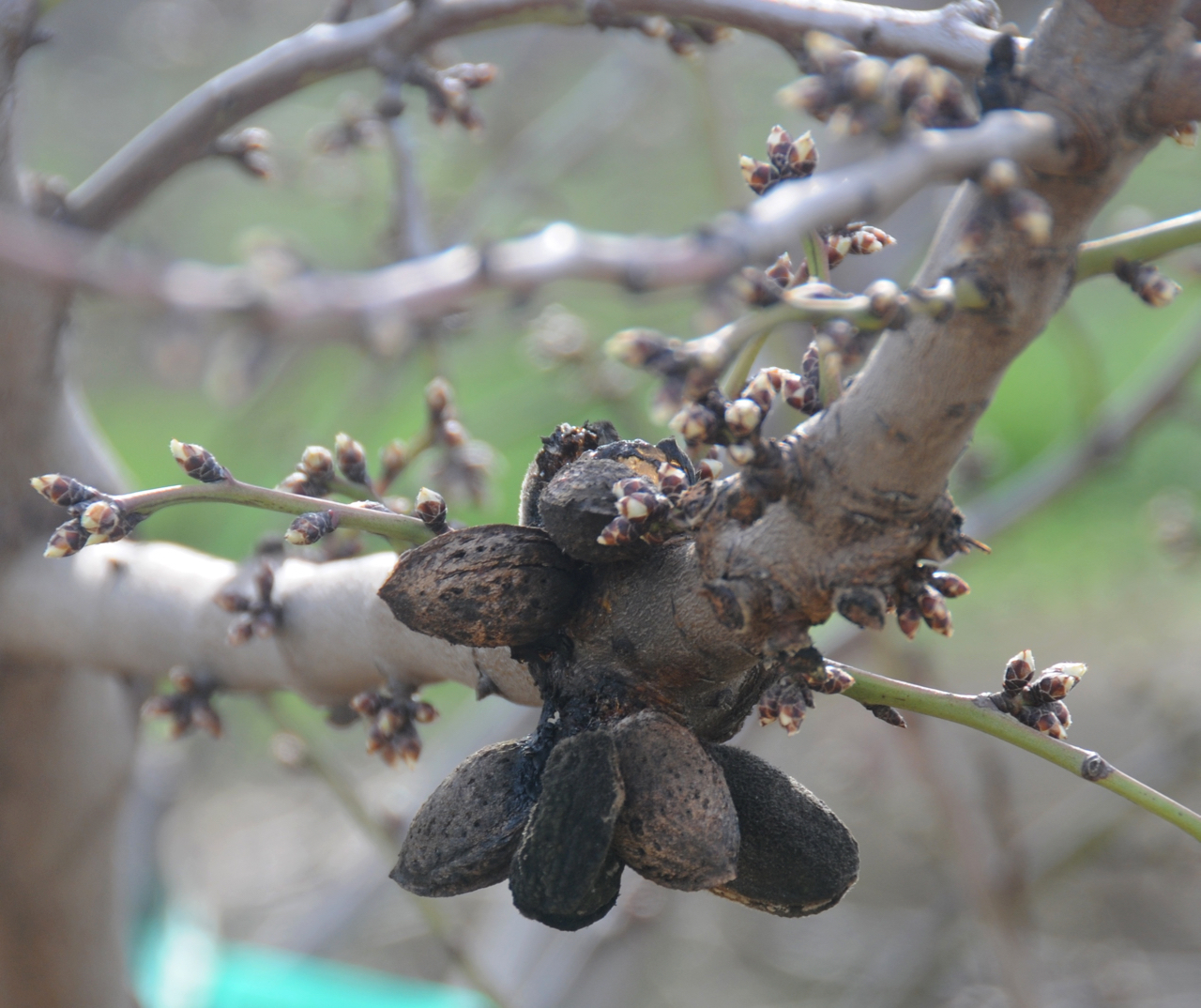
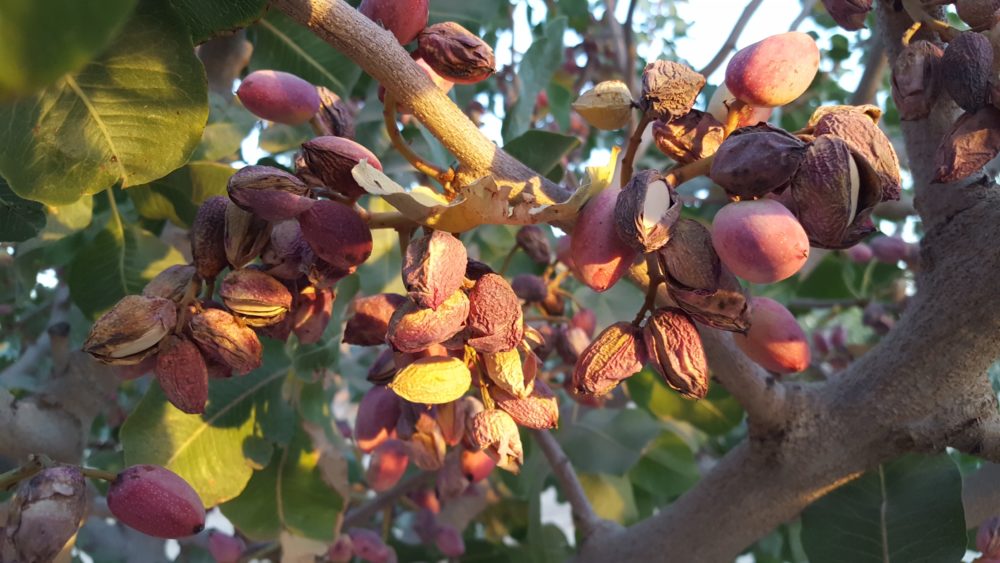
We tend to think that it can help rot the nuts and do us some favors, but we have to be able to get the nuts shaken or get pulling crews in and get the mummies on the ground and destroyed,” Symmes said.
Heat units also played a part in the development of more NOW.
“It got hot. And it seemed to just not let up. Our degree-day models, or the heat unit that drive insect development, ended up getting pretty far out ahead of what is typical,” Symmes explained.
“By September, we were about two weeks ahead in degree-days, and that which meant moths were out earlier. They’re flying around. They’re laying eggs on the nuts when they’re still on the trees, and we are talking almonds, pistachios and to a lesser extent, walnuts.”
Symmes said the importance of sanitation is to minimize the site where the NOWs mature.
“It’s really important to remember that sanitation efforts aren’t just directly killing any worms that are over-wintering in your orchard. But the other thing that it does is it minimizes those sites where the first and second generations are going to develop next year,” she said.
Despite all these circumstances as to why NOW was serious this this year, it is critically important to start orchard sanitation as soon as possible. It may not be a good idea to wait for rain and fog to help loosen the nuts this season.