Almond and Pistachio NOW Sanitation Critical This Winter
Joel Siegel on NOW Sanitation
By Patrick Cavanaugh, Farm News Director
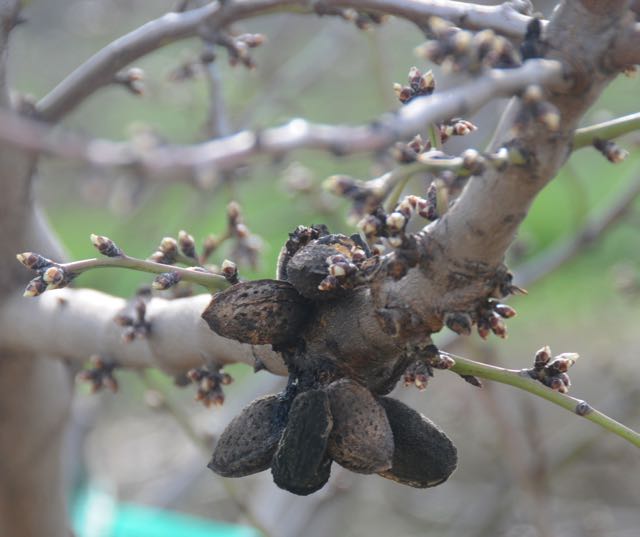
Last year was a bad year for navel orangeworm (NOW) mainly in pistachios, but also in almonds. If left in the trees, infested nuts become a great reservoir for more NOW to inhabit them.
Joel Siegel, a research entomologist for the USDA Agricultural Research Service based in Parlier, stresses the importance of having a good sanitation plan in place to remove those NOW mummy nuts. “When we talk about sanitation, it should be the foundation for everyone’s nut program. That’s something that you control.”
“In almonds, it’s absolutely essential. Where we’ve taken a look at it in the south, every infected mummy per tree is good for 1 percent damage. So going from one mummy to two mummies, your damage on average increases another 1 percent.”
“It’s also important to destroy the mummies on the ground. You figure, for every eight or nine mummies on the ground, that’s good for about a half a percent increase in damage. Get them off the tree and shred the almonds.”
Siegel noted that while pistachio growers can clear mummy nuts off the tree, the industry has not been able to shred the fallen pistachios effectively. The hard, rounded pistachio shells just bounce around in the shredder machine.
“What you can do is shake them off the tree as soon as possible so they’re on the ground where they can start rotting. You get those weeds growing around them. It has been shown that they break down faster in the weeds,” said Siegel.
“Growers disc them in. But if you’re going to disc them in, you have to disc them twice. Again, you’re not destroying the nuts, you are burying them so that NOW cannot lay eggs in the spring,” he said.
The risk of poor sanitation is high. Considerable NOW damage can prevent pistachio and almond growers from earning the premium paid for nuts that are pest-free.

















 In a ingenious effort to control the spread of the psyllid, t
In a ingenious effort to control the spread of the psyllid, t














