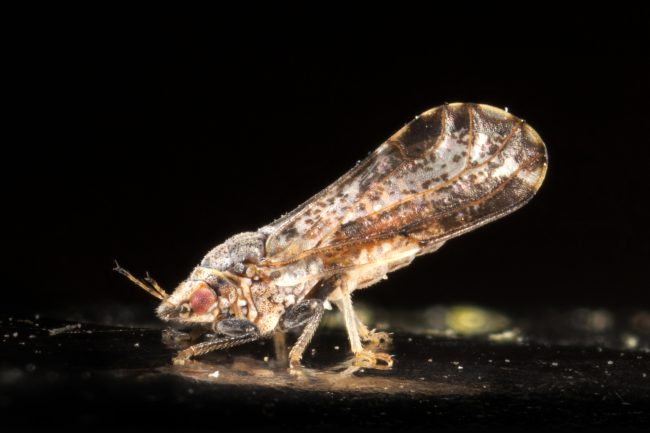
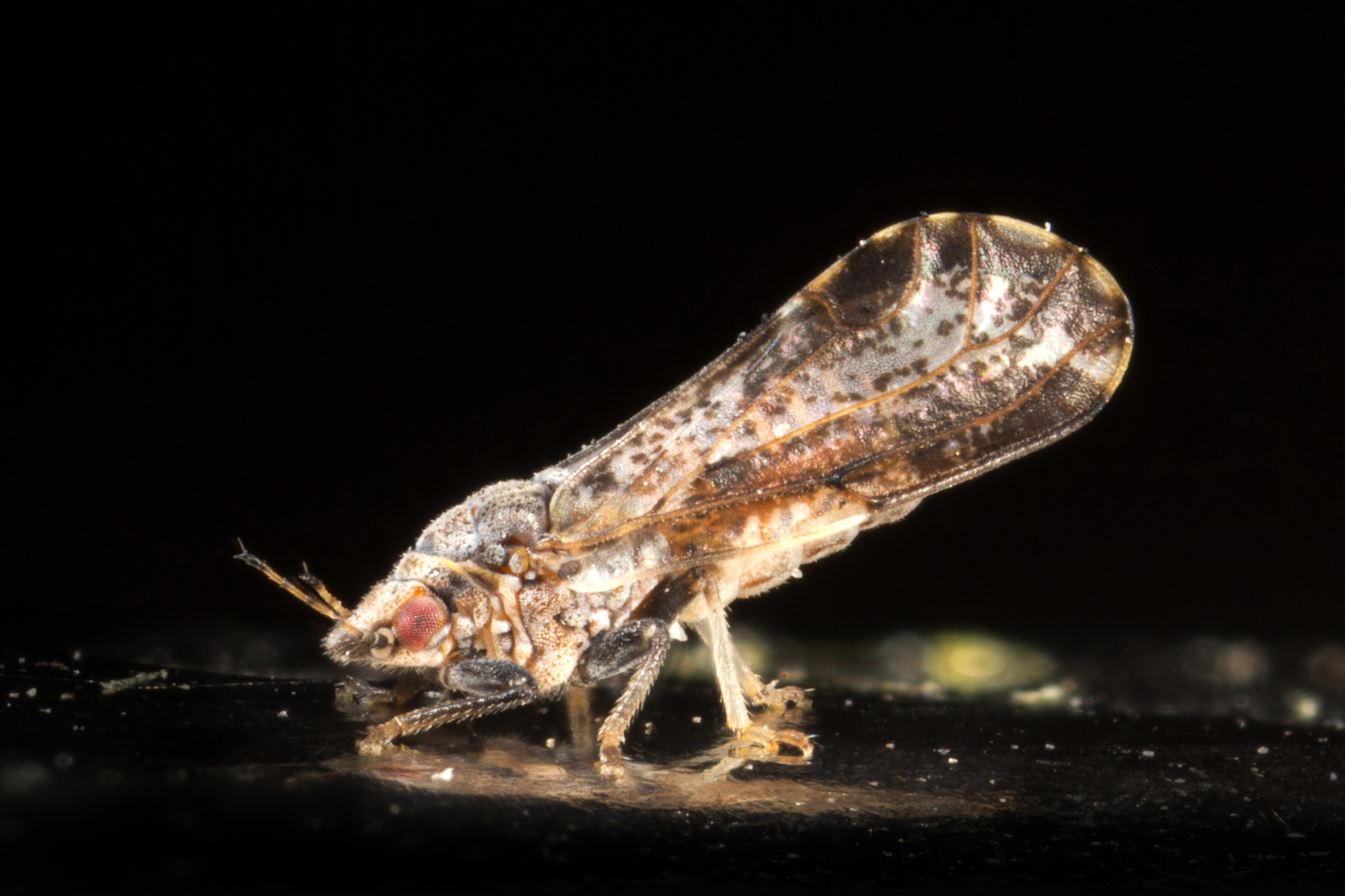
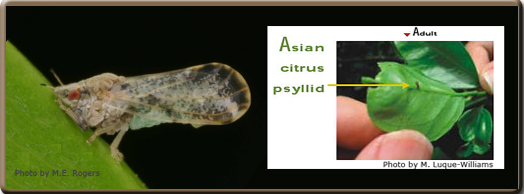
Quarantines in Place to Prevent ACP Spread
Quarantines Painful For Some Growers
By Mikenzi Meyers, Associate Editor
It’s been a tough road for citrus growers since the discovery of the Asian Citrus Psyllid (ACP) back in 2012. Those affected have been forced to quarantine their crops, a task that Beth Grafton-Cardwell, director of Lindcove Research Extension Center in Tulare and research entomologist with UC Riverdale, said can be difficult.
“There’s been a lot of discussion about the quarantines because they’ve been painful for some growers who have low psyllid numbers to have to treat them and move their fruit to other zones,” Cardwell explained.
The growing concerns have led to continuous research regarding whether or not the zones should be changed.
There have been more than 1,100 citrus trees that have tested positive for HLB. There have been more than 230 positive finds of the psyllid, and although this sounds like a big number, Cardwell said its actually normal due to how difficult the disease is to detect.
“We can’t tell that the tree is infected early on because a localized infection might be on one stem of the entire tree, and it might take a year before it moves throughout the tree,” she said.
Right now, quadrant sampling is being done, where four quadrants of the tree are sampled for the disease. Current samples are showing that one in four quadrants are coming back positive.
“It’s finding the trees that are infected that’s really difficult, and meanwhile, the psyllid is spreading, spreading, spreading the disease,” Cardwell said.
More information can be found at this link:
https://maps.cdfa.ca.gov/WeeklyACPMaps/HLBWeb/HLB_Treatments.pdf