Bayer CropScience Horticulture Symposium Builds Relationships
Bayer CropScience Horticulture Symposium Builds Global Relationships for Collaborative Problem-Solving
By Patrick Cavanaugh, Deputy Editor
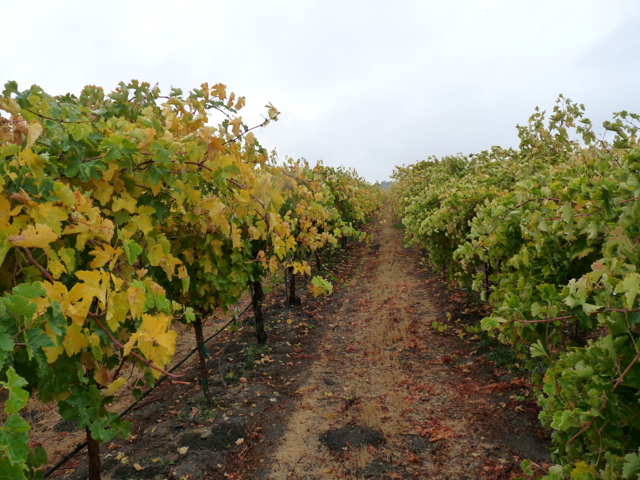
Nearly 200 professionals in the horticultural industry from across the food chain and the value chain, and from Europe and North, Central and South America, gathered this week at the Bayer CropScience Horticulture Symposium in Puerto Vallarta, Mexico. Attendees were treated to an inspirational mix of lectures, panel discussions, as well as an interactive poster session, all incorporating forward-thinking sustainable practices into contemporary agriculture. Among the crops discussed were tomatoes, citrus, grapes, potatoes, bananas.
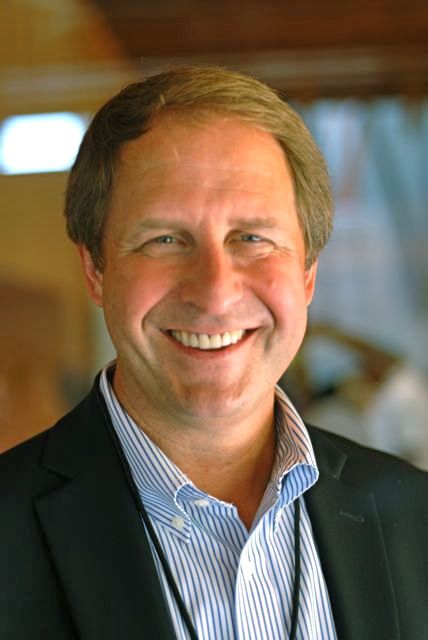
Rob Schrick, strategic management lead, Bayer CropScience Horticulture, based in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, said the event was the company’s second in a series of horticulture symposiums focused on international collaboration and problem-solving. “This is about bringing the best and brightest from across our industry,” said Schrick, “from influencers and universities to industry members like ourselves and the media. It’s about getting these creative minds together and discussing solutions. The solutions may not come from the symposium itself, but the connections that are made—you don’t know what will yield from those relationships.”
Jim Chambers, director of marketing, Bayer CropScience Food Production, said the Horticulture Symposium was all about sharing information on best management practices. “Bayer is a leader in the crop protection business within the horticultural space around the world, and this is a real opportunity to bring all of us within horticulture across the food chain and the value chain to talk, from the grower, to the processor, and to the consumer. It is a wonderful opportunity to work together to solve some very difficult challenges.”
“And, vivid to all attendees, was that members of the fruit and vegetable industry throughout the Americas have similar challenges to overcome,” noted Chambers. “It was very interesting; the issues that we talk and hear about in the specialty crop states such as California, Florida and Texas, are very much the same issues that people, for example in Mexico, Brazil, Argentina, or Central America, are facing. These issues do not go across just states or counties; they reach across the globe in solving these problems,” Chambers said.
Among the speakers were growers, commodity specialists from the industry and academia, and experts on sustainability practices, professionals on Maximum Residue Levels (MRLs), Bayer CropScience specialists and major agricultural association leaders such as Tom Nassif, ceo, Western Growers Association (WGA) and Dana Merrill, president, Mesa Vineyard Management Inc.
Bayer is a global enterprise with core competencies in the Life Science fields of health care and agriculture. Bayer CropScience, the subgroup of Bayer AG responsible for the agricultural business, is one of the world’s leading innovative crop science companies in the areas of seeds, crop protection and non-agricultural pest control. The company offers an outstanding range of products including high value seeds, innovative crop protection solutions based on chemical and biological modes of action as well as an extensive service backup for modern, sustainable agriculture.
(Photo features Rob Schrick, Bayer CropScience – Horticulture strategic management lead)