Blueberries
More Rain, More Fungi, More Use for Multiuse Fungicides
With More Rain, More Fungi, More Use for Multiuse Fungicides
By Patrick Cavanaugh, Deputy Editor
With spring rains, many vegetables, tree fruits, grapes and nuts succumb to fungi pressure. However, during the past few years, only trivial amounts of spring rain have moistened California’s soil and lulled farmers to abandon their vigilant watch for fungi proliferation. But now, the strong likelihood of El niño-driven wet weather this spring could catch growers off-guard.
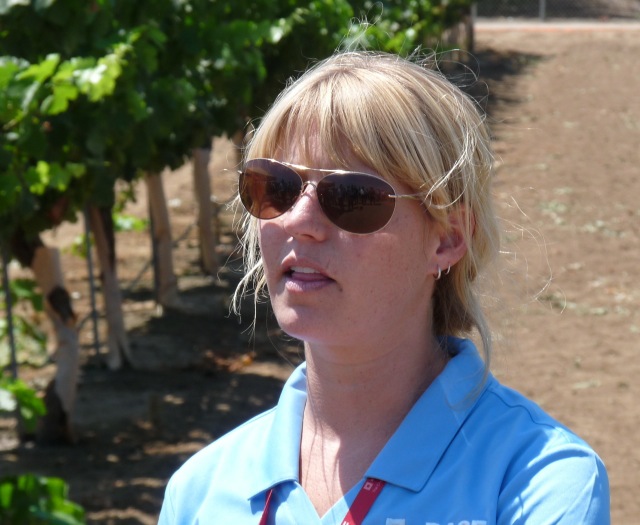
“We have an El niño coming that has already been tagged, ‘Too big to fail,’ which will bring a lot of rain. So it’s really important for folks to think about switching gears this year on their pest management mindset. With more rain, comes more fungi disease. We always see really high pressure disease years with rain,” said Kate Walker a technical services representative with BASF Corporation on the Central Coast, who advises use of a multiuse fungicide product already on hand.
Strawberries, in particular, are vulverable to fungi. “We have heard from our strawberry growers,” said Walker, “that these fungal diseases are always present in California, but they vary significantly in their severity year-to-year depending on the weather,” noted Walker.
“One major disease that accompanies higher moisture, Anthracnose, often called leaf, shoot, or twig blight,” Walker explained, “results from infection caused by the fungus Colletotrichum. I’ve heard some growers have not experienced Anthracnose issues in 10 years,” said Walker. “As it emerges and becomes more problematic in strawberries, farmers really need to know which types of fungicides to use to manage this and other diseases.”
“It is very important for farmers and PCAs to walk through and scout their fields for disease,” Walker said, “and when they identify one, to become very aggressive with their fungicide management program. So, as representatives for BASF, we are lucky to have multiuse fungicide products available to control these diseases, such as Merivon Fungicide.”
Walker noted Merivon has two modes of action, “so it is very broad-spectrum. Typically we position Merivon in California for use on powdery mildew and Botrytis, but what we seldom talk to growers about is its utility for Anthracnose. We see a lot more Anthracnose in Florida and on the East Coast due to the increased rains; whereas, it usually doesn’t come through every year in California. So it is good to for farmers and PCSs to know that the product with which they are familiar for use in Botrytis, is also very effective with other issues, like Anthracnose.”
Walker offered, “Another very common disease that flourishes with increased rain, Rhizopus, occurs post-harvest, after the berries are picked up from the field. Again, Merivon has utility for Rhizopus as well, so growers don’t have to change or reinvent their program to manage these diseases.”
Walker said, “Rhizopus is an airborne bread mold. It is very common in the air and in the soil, so anytime a fruit or a nut is exposed to the spores blowing in the wind, it is vulnerable to infection with this disease.”