Water Diversion Plan for Fish, Part 2
Grober: It Won’t Help to Vilify People
Part 2 of 2-part Series
By Patrick Cavanaugh, Farm News Director
California Ag Today conducted an extensive interview with Les Grober, assistant deputy director, State Water Resources Control Board (SWRCB, Water Board) Division of Water Rights. We published Part 1, “Water Board’s Point of View on Increasing San Joaquin River Flows,” on November 28, 2016.
http://yn2.000.myftpupload.com/increasing-san-joaquin-river-flows/
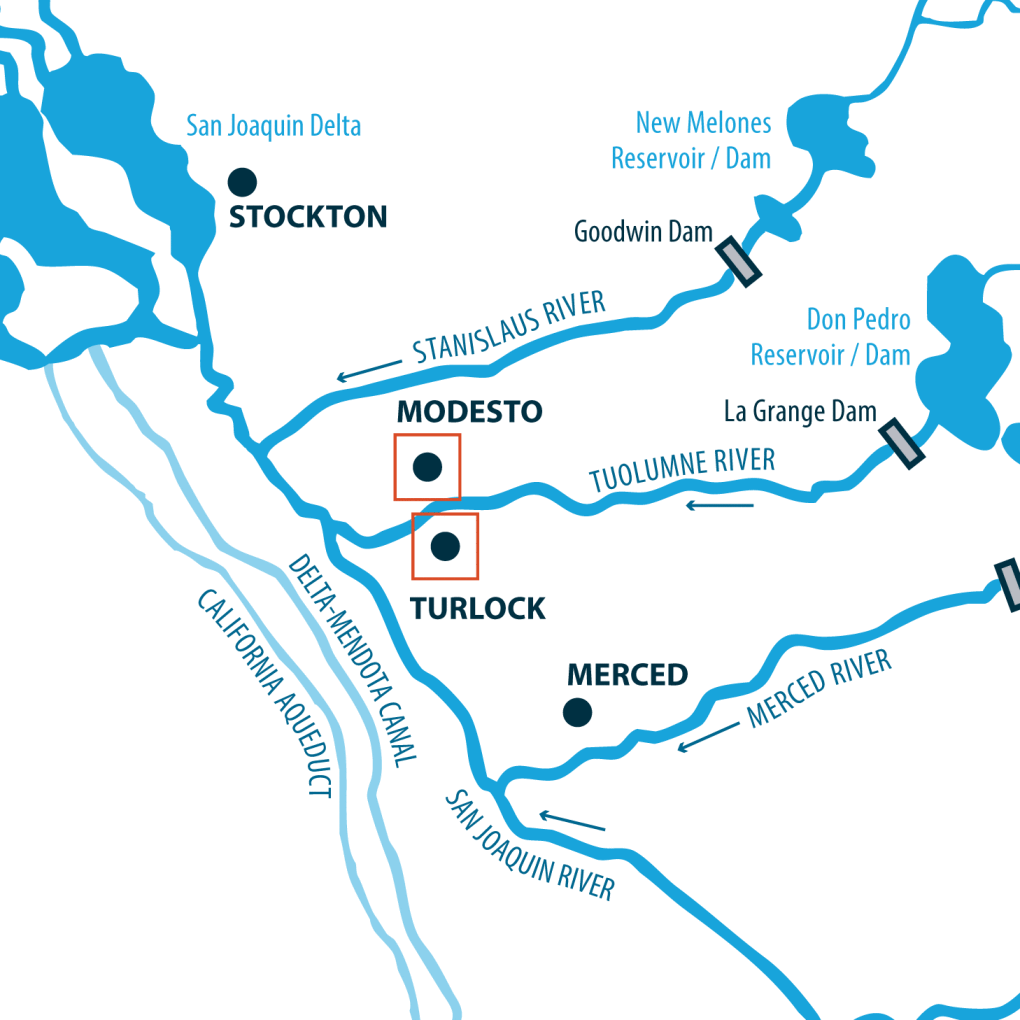
Grober explained the Water Board’s water diversion plan to adjust the flow objectives on the San Joaquin River to protect fish and wildlife. The plan, specifically, is to divert 40 percent of water flows from the Stanislaus, Tuolumne and Merced Rivers that flow into the lower San Joaquin River.
California Ag Today: We asked Mr. Grober to explain how the Federal Water users on the Westside of Fresno and Kings Counties were granted a mere 5 percent allocation this year, and why many did not receive their full 5 percent.
Grober: The 5 percent allocation is due to the junior water rights of those growers and to the interconnections of so many things — priority of right, hydrologic conditions, and minimal protections or fish and wildlife. Anyone who thinks it’s all due to fish is simplifying a very complex situation.
California Ag Today: Regarding the water hearings that are scheduled over the next few months, is the Water Board trying to give information to farmers and others would be affected by the decreased water should the Water Board’s proposal go through?
Grober: The ultimate goal is to make people even more prepared to provide comments to the Board at the scheduled hearings. It’s part of a public process where, if we did not get our economic figures right, we want [accurate] information from the stakeholder to make it right.
We thought we did a good job in an economic analysis on how we thought the proposed taking of 40 percent water would affect the communities and farmers. We clearly heard from many people who thought we did not do a good job, and my response is: Good, show us why, make a proposal and take it to the Water Board hearings, and then we can adjust it.
California Ag today: The Water Board has a 3,100-page report all about saving the salmon.
Grober: The reason we have a big report is because we are making a proposal and we’ve shown our work. Although it is work for people to look at it and review it, we have tried to make it easy so that people can see if we have made mistakes, if there are things that are left out or if we have made an incorrect assumption. That’s why we’ve shared it with everybody and here’s your opportunity for setting us straight.
It won’t help to vilify different people who are making good use of the water or to vilify or disparage the implementation of our laws and what we are required to do. We have a great process I think, as hard as it is, a public process where we can work these things out in the open, just to use it and deal with each other professionally.
-Les Grober, assistant deputy director, State Water Resources Control Board (SWRCB, Water Board) Division of Water Rights
California Ag Today: We are sure you are getting a lot of information from farmers and city leaders about this not being a good use of the water.
Grober: These problems are not so simple that they could be reduced to a sound bite. I think we would have solved the salmon problems by now, but because we are in the drought situation, we are dealing with a precious resource, which is water. Everybody wants the water but there’s not enough to do all the things we would like to do with it.
California Ag Today: But there are many people in California who feel that more water for fish instead of farmers is reprehensible.
Grober: It won’t help to vilify different people who are making good use of the water or to vilify or disparage the implementation of our laws and what we are required to do. We have a great process I think, as hard as it is, a public process where we can work these things out in the open, just to use it and deal with each other professionally.
California Ag Today: But we’ve heard from experts that have been studying this, that the increased flows have not really helped these species. Do you have proof that they have?
Grober: It’s hard to show proof one way or the other because recently we have not increased flows to see what effect it would have. That seems to be a notion that is out there, that we have somehow done something to increase flows in recent years, and that’s simply not the case.
If anything, flows have gone down. And in the recent drought years, as I said, even the minimal flows that were required were adjusted downward. You would have to show me that evidence that flows have gone up and there has been no response to those higher flows. I do not believe that there is any.
California Ag Today: So, the Water Board wants 40 percent of unimpaired flows?
Grober: When we say the requirement is 30 percent to 50 percent of unimpaired flows, it is 30 percent to 50 percent of that amount, which means just the opposite. It means that 50 to 70 percent of [flows] for February through June would be available for consumptive use.
That is frequently misunderstood and turned around. That is still from February through June, so it means more than 50 to 70 percent since other times of the year this water is available for consumptive use.
California Ag Today: Is the Water Board looking at the fact that if the water is needed for the species, it is going to force these growers to use more groundwater? That is a direction in which we do not want to go, especially in a region that has not yet had critical overdrafts. How does the Water Board look at that domino effect forced on these growers in order to survive, stay in business and produce the food in this major Ag production region?
Grober: Implementing that 30 to 50 percent of unimpaired flows would mean less surface water available for diversion. So our analysis of the potential environmental effects and overall effects of the program, based on recent drought information and other information, shows we would see increased groundwater pumping.
California Ag Today: Is the increased pumping weighted at all in the proposal, because overdraft groundwater pumping is not sustainable?
Grober: By our analysis, the area is already in overdraft.
California Ag Today: What? Why would there be overdraft pumping in an area that has great irrigation districts such as Modesto and Oakdale Irrigation Districts delivering surface water? We did not think growers in those districts would be overdrafting.
Grober: Sure. Within those irrigation districts themselves, they are not overdrafting. That’s why the analysis we do goes into that level of detail. The irrigation districts that already have a source of surface water actually apply much more water than they need just for the crop, so they are recharging groundwater within those districts, and even with this proposal, would continue to recharge groundwater. It is all those areas outside of those districts that don’t have access to surface water that are pumping groundwater.
California Ag Today: There is a lot more pumping of groundwater on the east side near the foothills.
Grober: Based on the information that we have, the total area — not just the districts that have access to surface water — but the total area, is already overdrafting groundwater. And there are many areas on the east side of these districts now, up into areas that were previously not irrigated, converting now to orchard crops. So with the information we have, there are large areas of production using water from the basin. The entire area is to some extent pumping more groundwater than there is recharge.
California Ag Today: We’ve been concern about this.
Grober: That’s why the Sustainable Groundwater Management Act (SGMA) is going to be good, because the local areas are going to have to get on top of that information and on top of the management.