New Medfly Quarantine
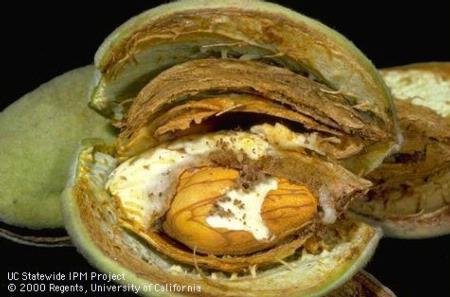
A portion of San Diego County was placed under Medfly quarantine earlier this week following the detection of 4 adult Mediterranean fruit flies (Medflies) in the La Mesa area. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), the San Diego County Agricultural Commissioner, and CDFA are working collaboratively on this project.
The quarantine area in San Diego County measures 93 square miles, bordered on the north by Prospect Avenue; on the south by Mount Miguel Road; on the west by Fairmount Avenue; and on the east by Vista Grande Road. A link to the quarantine map may be found here: www.cdfa.ca.gov/plant/
To eradicate the infestation, the release of sterile male Medflies began on August 10, at a rate of 250,000 flies per square mile per week. The new release area is approximately 59 square miles. In addition, properties within 200 meters of detections are being treated with an organic formulation of Spinosad, which originates from naturally-occurring bacteria in soil, in order to eliminate any mated females and reduce the density of the population. Finally, fruit removal will occur within 100 meters of detection properties in order to remove any fruit infested with eggs and larvae.
The quarantine will affect any growers, wholesalers, and retailers of susceptible fruit in the area as well as local residents. Home gardeners are urged to consume homegrown produce on site and not move it from their property. These actions protect against the artificial spread of the infestation to nearby regions where it could affect California’s food supply and our backyard gardens and landscapes.
In the eradication program, sterile male Medflies are brought to San Diego County from the joint CDFA/USDA sterile insect rearing facility in Los Alamitos, which prepares sterile files for release everyday over the Los Angeles basin. The sterile release program has a proven track record of eradication in southern California. Sterile male flies mate with fertile female flies in the environment but produce no offspring. The Medfly population decreases as the wild flies reach the end of their natural life span with no offspring to replace them, ultimately resulting in the eradication of the pest.
The Medfly can infest more than 250 types of fruits and vegetables, causing severe impacts on California agricultural exports and backyard gardens alike. Residents who believe their fruits and vegetables are infested with fruit fly larvae are encouraged to call the state’s toll-free Pest Hotline at 1-800-491-1899.