BREAKING NEWS ON HUANGLONGBING CITRUS DISEASE
HUANGLONGBING CITRUS DISEASE DETECTED IN SAN GABRIEL AREA OF LOS ANGELES COUNTY
CDFA
Release #15-031
Sacramento, July 10, 2015 – The California Department of Food and Agriculture (CDFA) and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) have confirmed detection of huanglongbing (HLB) citrus disease, or citrus greening. The disease was detected in plant material taken from a kumquat tree in a residential neighborhood in the San Gabriel area of Los Angeles County.
This is the second time HLB has been detected in California. The first detection occurred in 2012 in a residential citrus tree in Hacienda Heights, about 15 miles from San Gabriel.
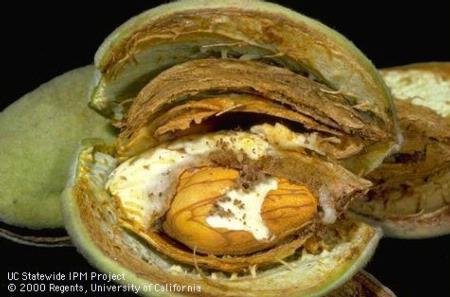
HLB is a bacterial disease that attacks the vascular system of plants. It does not pose a threat to humans or animals. The Asian citrus psyllid (ACP) can spread the bacteria as the pest feeds on citrus trees and other plants. Once a tree is infected, there is no cure; it typically declines and dies within a few years.
“Citrus is a cherished part of our landscape and our shared history, as well as a major agricultural crop,” said CDFA Secretary Karen Ross. “CDFA is moving quickly to protect the state’s citrus. We have been planning and preparing for HLB detections with our growers and our colleagues at the federal and local levels since before the ACP was first detected here in 2008.”
A CDFA crew has removed and disposed of the infected tree and is preparing to conduct treatment of citrus trees for ACP infestation within 800 meters of the find site. By taking these steps, a critical reservoir of disease and its vectors will be removed, which is essential.
An intensive survey

SAVE OUR CITRUS app is a free USDA iPhone to report and identify the four leading citrus diseases: citrus greening, citrus canker, citrus black spot and sweet orange scab. Report your symptoms, upload a photo and citrus experts will respond.
quarantine, citrus and closely related plants at nurseries in the area will be placed on hold.
Residents of quarantine areas are urged not to remove or share citrus fruit, trees, clippings/grafts or related plant material. Citrus fruit may be harvested and consumed on-site.
CDFA, in partnership with the USDA, local agricultural commissioners and the citrus industry, continues to pursue a strategy of controlling the spread of ACPs while researchers work to find a cure for the disease.
HLB is known to be present in Mexico and in parts of the southern U.S. Florida first detected the pest in 1998, and the disease in 2005, and the two have now been detected in all 30 citrus-producing counties in that state. The University of Florida estimates that the disease causes an average loss of 7,513 jobs per year, and has cost growers $2.994 billion in lost revenue since HLB was first detected in that state in 2006.
HLB has also been detected in Georgia, Louisiana, South Carolina and Texas, as well as Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands. A total of 15 states or territories are under full or partial quarantine due to the detected presence of the Asian citrus psyllid: Alabama, American Samoa, Arizona, California, Florida, Georgia, Guam, Hawaii, Louisiana, Mississippi, Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico, South Carolina, Texas, and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
The ACP was first detected in California in 2008, and quarantines are now in place in 17 California counties. If Californians have questions about the ACP or HLB, they may call CDFA’s toll-free pest hotline at 1-800-491-1899 or visit: http://www.cdfa.ca.gov/phpps/acp/.