Early Rain Caused Concern for Butte County Rice Growers
Butte County Rice Growers Respond to Early Rain
By Brian German, Associate Broadcaster
The Butte County Farm Bureau has been working to protect agriculture’s interests since 1917, thanks in large part to the continued hard work of their members. With continued support, the Bureau is able to advocate for growers on important issues in the community and fund educational opportunities.
Colleen Cecil, executive director of the Bureau, observed the rice harvest looks strong for Butte County rice growers, but a weather-related issue caused a bit of a problem during harvest. “We had some wet weather and then we had a break. Then it was, ‘Hurry up and get it done before the next storm comes in,’” said Cecil.
While the weather was an issue for growers, its impact was minimal. “There was a percentage, somewhere in the teens likely, of rice that was still left out in the field after the last wet weather event [in which] we just got pounded with rain,” Cecil noted.
“Water shortages over the past couple of years had forced many rice growers in Northern California to cut back on overall production. However earlier this year, as a result of improved rainfall last winter, growers went back to planting a more average level of rice. Those fields that had been taken out of production had a good amount of rest, and are now producing nicely once again.”
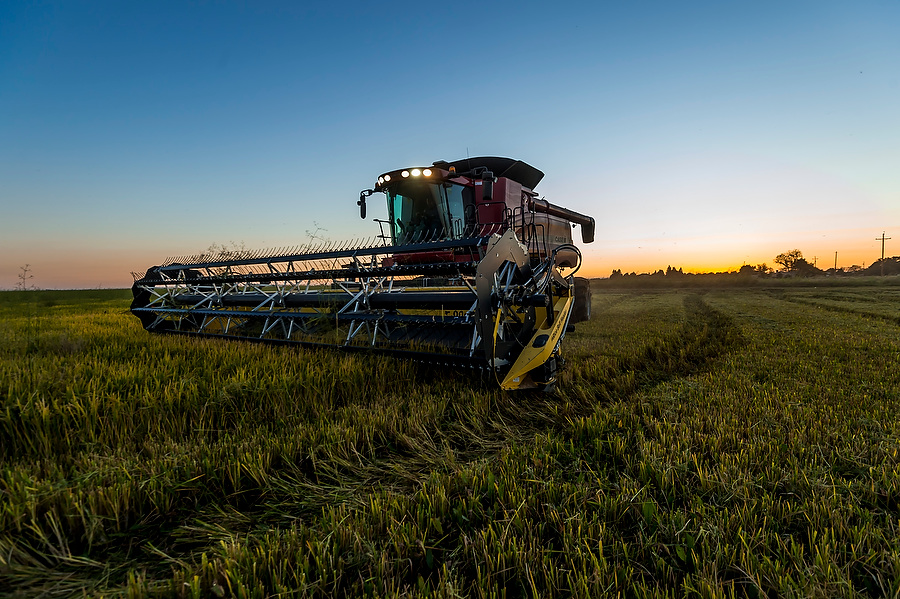
Though not uncommon, growers may have adjusted their harvest schedule in response to the early winter rain. “While it does happen on occasion, it is not ideal for farmers to harvest rice after wet weather all the time. It goes more slowly, it becomes a little messier, and it requires a transition from tires to tracks on their harvesting equipment. Again, it slows it down,” Cecil said.
“In 2013, the average rice grower in Butte County was producing just under 90 sacks per acre, with each sack weighing the [approximately] 100 pounds. Butte County has close to 88 thousand bearing acres of rice. While the local industry remains strong, early rainy weather can put a dent in production.”
Cecil explained, “It wasn’t that they couldn’t get [the rice] out, it was that the crop wasn’t ready to come out. There was still a tremendous amount of moisture in it and it wasn’t at the right percentage of moisture to take out of the field, so they had to wait.”
Last year’s crop report shows that Butte County’s five most valuable crops were walnuts, almonds, rice, prunes and peaches. The area’s walnut crop alone was valued at just under $241 million dollars. Cecil said this year’s harvest, “the almonds came off without a hitch. The walnuts got tagged at the end with the wet weather, but I don’t think it slowed everybody down,” Cecil said.
Featured Photo: Richard and Laurel Nelson’s Farm, Twin Creek Ranch, on Pleasant Grove Road and Marcum, Thursday, September 29, 2016.
Photo Courtesy of California Rice Commission/Brian Baer Photography