A Challenge Regarding NOW Monitoring
NOW Monitoring Challenged This Season
By Patrick Cavanaugh, Farm News Director
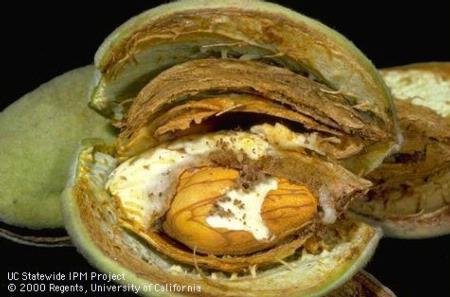
Navel orangeworm (NOW) is the number one pest in almonds and pistachios. There are many tools to monitor and control it, and ironically, one tool is making it difficult for researchers to understand the pressure in the orchards. Joel Siegel, a research entomologist with USDA ARS in Parlier in Fresno County, spoke with California Ag Today about the issues in NOW monitoring.
“One of the problems now is so many people are using mating disruption that it’s shutting down the pheromone traps, so I don’t have reliable trap data anymore. I have my own traps. Most of them are at zero,” Siegel said. “That could mean no caught navel orangeworm adults.”
“I have some traps that are catching, so I would tell people that the population is on the upswing now. We’re coming up to 2700 degree-days in a lot of locations,” he said.
That degree-day number represents the amount of accumulated heat units, or higher temperatures to push the pest to a new generation. NOW mating disruption is a strategy where the female pheromone is spread through the orchard through special aerosol emitters, and the widespread pheromone confuses the males because of the high pheromone concentration and thus, no mating.
“When you have mating disruption nearby, it interferes with the NOW traps,” he said.
The pheromone trap attracts males to it and gives researchers an idea of the concentration of the males in the orchard. No trapping of males? Then you really don’t know the numbers in the orchard.
“The PCAs are going back to a lot of their traditional methods, such as egg traps instead,” Siegel said. “Time will tell if navel orangeworm pressure is great this year.”