Food Safety Modernization Act
Food Safety In the Produce Supply Chain
Food Safety is Paramount in Produce Industry
By Tim Hammerich, with The Ag Information Network of the West
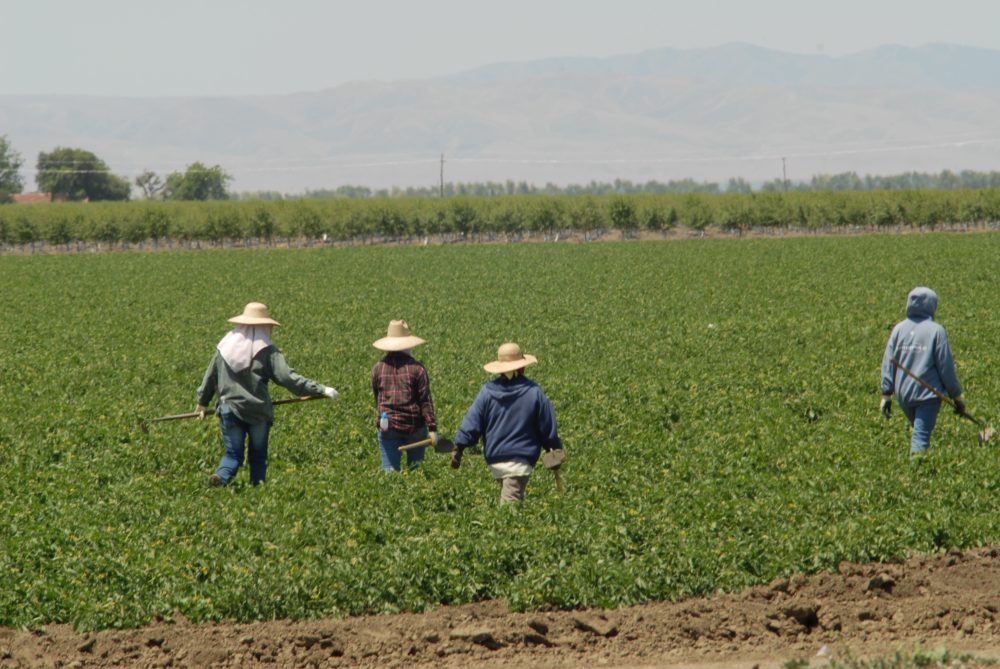
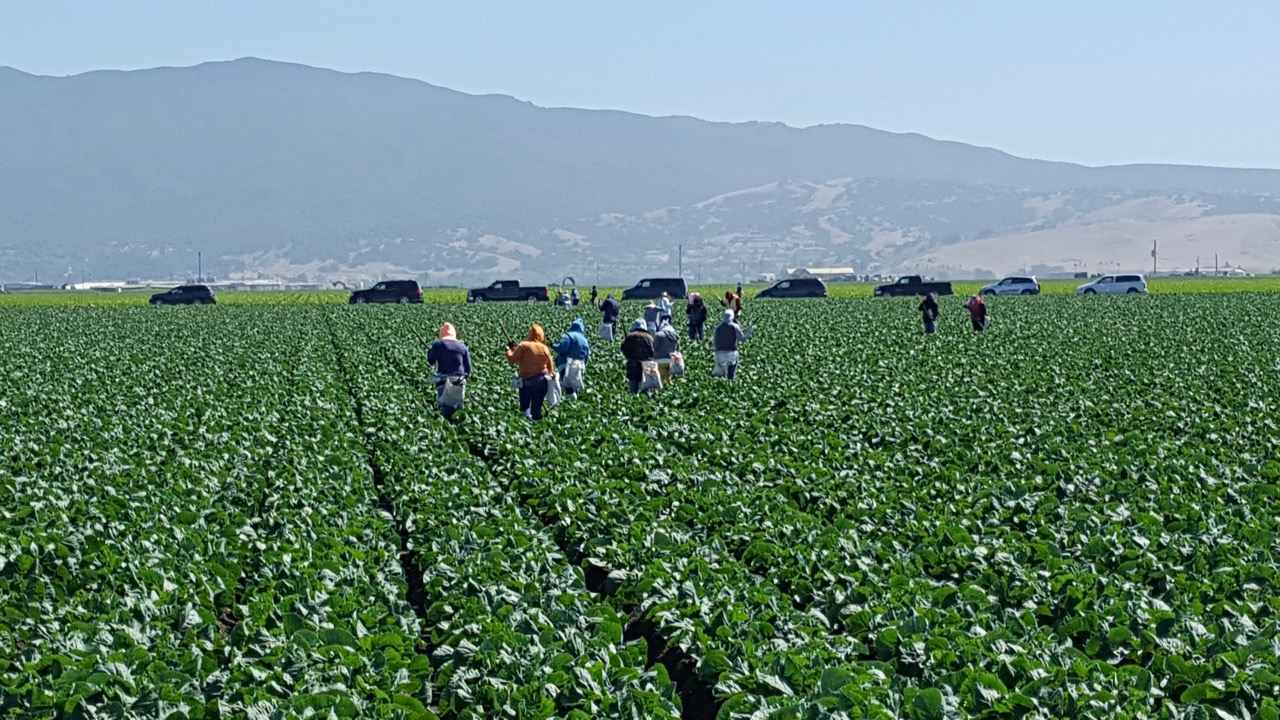
Food safety is something everyone in the produce industry is concerned about, from growers all the way through the supply chain.
United Fresh Produce Association is a trade group that exists to empower produce industry leaders to join forces to shape sound government policy. California Ag Today’s Patrick Cavanaugh caught up with United Fresh President and CEO Tom Stenzel at the association’s Fresh Start Conference in Tucson.
“We’ve got to do a better job in traceability We’ve got to be able to get to the source of these issues right away. You know, our products are grown outside in nature,” said Stenzel. “There’s no kill step. We don’t cook our salads. So we’re probably never going to get to zero, but we’re going to keep getting better in prevention and then we’ve got to do better tracing it back.”
That traceability aspect can be a challenge in complex supply chains like those of some fresh produce. But Stenzel says their members are committed to finding innovative solutions.
“So the grower/shipper community, they’re trying to figure out how do I prevent food safety issues. And we’re learning a lot. Every time there’s an outbreak, as tragic as it is, we learn from it. And that’s really what the growers are trying to do right now, is to take every possible step of precaution in how they use water; or how they use compost,” said Stenzel. Making sure that we’re not contributing to contamination. Wholesalers, retailers, everybody’s got to work together on those things.”
Stenzel said just about every meeting they had around the Fresh Start Conference addressed some aspect of food safety.